
Gould John Mead
How to Camp Out
OTHER WAYS OF GOING AFOOT
It is not necessary to say much about the other ways of going afoot. If you can safely dispense with cooking and carrying food, much will be gained for travel and observation. The expenses, however, will be largely increased. If you can also dispense with camping, you ought then to be able to walk fifteen or twenty miles daily, and do a good deal of sight-seeing besides. You should be in practice, however, to do this.
You must know beforehand about your route, and whether the country is settled where you are going.
Keep in mind, when you are making plans, that it is easier for one or two to get accommodation at the farmhouses than for a larger party.
I heard once of two fellows, who, to avoid buying and carrying a tent, slept on hay-mows, usually without permission. It looks to me as if those young men were candidates for the penitentiary. If you cannot travel honorably, and without begging, I should advise you to stay at home.
CHAPTER III
LARGE PARTY TRAVELLING AFOOT WITH BAGGAGE-WAGON
With a horse and wagon to haul your baggage you can of course carry more. First of all take another blanket or two, a light overcoat, more spare clothing, an axe, and try to have a larger tent than the "shelter."
If the body of the wagon has high sides, it will not be a very difficult task to make a cloth cover that will shed water, and you will then have what is almost as good as a tent: you can also put things under the wagon. You must have a cover of some sort for your wagon-load while on the march, to prevent injury from showers that overtake you, and to keep out dust and mud. A tent-fly will answer for this purpose.
You want also to carry a few carriage-bolts, some nails, tacks, straps, a hand-saw, and axle-wrench or monkey-wrench. I have always found use for a sail-needle and twine; and I carry them now, even when I go for a few days, and carry all on my person.
The first drawback that appears, when you begin to plan for a horse and wagon, is the expense. You can overcome this in part by adding members to your company; but then you meet what is perhaps a still more serious difficulty,—the management of a large party.
Another inconvenience of large numbers is that each member must limit his baggage. You are apt to accumulate too great bulk for the wagon, rather than too great weight for the horse.
Where there are many there must be a captain,—some one that the others are responsible to, and who commands their respect. It is necessary that those who join such a party should understand that they ought to yield to him, whether they like it or not.
The captain should always consult the wishes of the others, and should never let selfish considerations influence him. Every day his decisions as to what the party shall do will tend to make some one dissatisfied; and although it is the duty of the dissatisfied ones to yield, yet, since submission to another's will is so hard, the captain must try to prevent any "feeling," and above all to avoid even the appearance of tyranny.
System and order become quite essential as our numbers increase, and it is well to have the members take daily turns at the several duties; and during that day the captain must hold each man to a strict performance of his special trust, and allow no shirking.
After a few days some of the party will show a willingness to accept particular burdens all of the time; and, if these burdens are the more disagreeable ones, the captain will do well to make the detail permanent.
Nothing tends to make ill feeling more than having to do another's work; and, where there are many in a party, each one is apt to leave something for others to do. The captain must be on the watch for these things, and try to prevent them. It is well for him, and for all, to know that he who has been a "good fellow" and genial companion at home may prove quite otherwise during a tour of camping. Besides this, it is hardly possible for a dozen young men to be gone a fortnight on a trip of this kind without some quarrelling; and, as this mars the sport so much, all should be careful not to give or take offence. If you are starting out on your first tour, keep this fact constantly in mind.
Perhaps I can illustrate this division of labor.
We will suppose a party of twelve with one horse and an open wagon, four tents, a stove, and other baggage. First, number the party, and assign to each the duties for the first day.
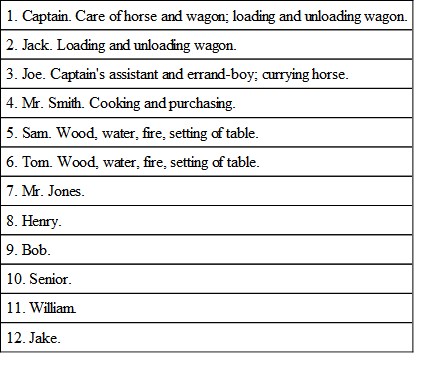
The party is thus arranged in four squads of three men each, the oldest at the heads. One half of the party is actively engaged for to-day, while the other half has little to do of a general nature, except that all must take turns in leading the horse, and marching behind the wagon. It is essential that this be done, and it is best that only the stronger members lead the horse.
To-morrow No. 7 takes No. 1's place, No. 8 takes No. 2's, and so on; and the first six have their semi-holiday.
In a few days each man will have shown a special willingness for some duty, which by common consent and the captain's approval he is permitted to take. The party then is re-organized as follows:—
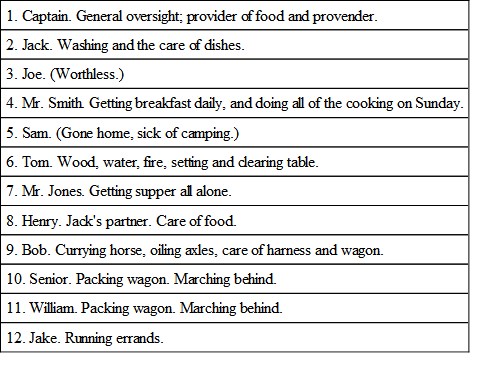
The daily detail for leading the horse will have to be made, as before, from the stronger members of the party; and if any special duty arises it must still be done by volunteering, or by the captain's suggestion.
In this arrangement there is nothing to prevent one member from aiding another; in fact, where all are employed, a better feeling prevails, and, the work being done more quickly, there is more time for rest and enjoyment.
To get a horse will perhaps tax your judgment and capability as much as any thing in all your preparation; and on this point, where you need so much good advice, I can only give you that of a general nature.
The time for camping out is when horses are in greatest demand for farming purposes; and you will find it difficult to hire of any one except livery-stable men, whose charges are so high that you cannot afford to deal with them. You will have to hunt a long time, and in many places, before you will find your animal. It is not prudent to take a valuable horse, and I advise you not to do so unless the owner or a man thoroughly acquainted with horses is in the party. You may perhaps be able to hire horse, wagon, and driver; but a hired man is an objectionable feature, for, besides the expense, such a man is usually disagreeable company.
My own experience is, that it is cheaper to buy a horse outright, and to hire a harness and wagon; and, since I am not a judge of horse-flesh, I get some friend who is, to go with me and advise. I find that I can almost always buy a horse, even when I cannot hire. Twenty to fifty dollars will bring as good an animal as I need. He may be old, broken down, spavined, wind-broken, or lame; but if he is not sickly, or if his lameness is not from recent injury, it is not hard for him to haul a fair load ten or fifteen miles a day, when he is helped over the hard places.
So now, if you pay fifty dollars for a horse, you can expect to sell him for about twenty or twenty-five dollars, unless you were greatly cheated, or have abused your brute while on the trip, both of which errors you must be careful to avoid. It is a simple matter of arithmetic to calculate what is best for you to do; but I hope on this horse question you may have the benefit of advice from some one who has had experience with the ways of the world. You will need it very much.
WAGONS
If you have the choice of wagons, take one that is made for carrying light, bulky goods, for your baggage will be of that order. One with a large body and high sides, or a covered wagon, will answer. In districts where the roads are mountainous, rough, and rocky, wagons hung on thoroughbraces appear to suit the people the best; but you will have no serious difficulty with good steel springs if you put in rubber bumpers, and also strap the body to the axles, thus preventing the violent shutting and opening of the springs; for you must bear in mind that the main leaf of a steel spring is apt to break by the sudden pitching upward of the wagon-body.
It has been my fortune twice to have to carry large loads in small low-sided wagons; and it proved very convenient to have two or three half-barrels to keep food and small articles in, and to roll the bedding in rolls three or four feet wide, which were packed in the wagon upon their ends. The private baggage was carried in meal-bags, and the tents in bags made expressly to hold them; we could thus load the wagon securely with but little tying.
For wagons with small and low bodies, it would be well to put a light rail fourteen to eighteen inches above the sides, and hold it there by six or eight posts resting on the floor, and confined to the sides of the body.
Drive carefully and slowly over bad places. It makes a great deal of difference whether a wheel strikes a rock with the horse going at a trot, or at a walk.
HARNESS
If your load is heavy, and the roads very hard, or the daily distance long, you had better have a collar for the horse: otherwise a breastplate-harness will do. In your kit of tools it is well to have a few straps, an awl, and waxed ends, against the time that something breaks. Oil the harness before you start, and carry about a pint of neat's-foot oil, which you can also use upon the men's boots. At night look out that the harness and all of your baggage are sheltered from dew and rain, rats and mice.
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF THIS MODE OF TRAVEL
This way of travelling is peculiarly adapted to a party of different ages, rather than for one exclusively of young men. It is especially suitable where there are ladies who wish to walk and camp, or for an entire family, or for a school with its teachers. The necessity of a head to a party will hardly be recognized by young men; and, even if it is, they are still unwilling, as a general rule, to submit to unaccustomed restraint.
The way out of this difficulty is for one man to invite his comrades to join his party, and to make all the others understand, from first to last, that they are indebted to him for the privilege of going. It is then somewhat natural for the invited guests to look to their leader, and to be content with his decisions.
The best of men get into foolish dissensions when off on a jaunt, unless there is one, whose voice has authority in it, to direct the movements.
I knew a party of twenty or more that travelled in this way, and were directed by a trio composed of two gentlemen and one lady. This arrangement proved satisfactory to all concerned.5
It has been assumed in all cases that some one will lead the horse,—not ride in the loaded wagon,—and that two others will go behind and not far off, to help the horse over the very difficult places, as well as to have an eye on the load, that none of it is lost off, or scrapes against the wheels. Whoever leads must be careful not to fall under the horse or wagon, nor to fall under the horse's feet, should he stumble. These are daily and hourly risks: hence no small boy should take this duty.6
CHAPTER IV
CLOTHING
If your means allow it, have a suit especially for the summer tour, and sufficiently in fashion to indicate that you are a traveller or camper.
SHIRTS
Loose woollen shirts, of dark colors and with flowing collars, will probably always be the proper thing. Avoid gaudiness and too much trimming. Large pockets, one over each breast, are "handy;" but they spoil the fit of the shirt, and are always wet from perspiration. I advise you to have the collar-binding of silesia, and fitted the same as on a cotton shirt, only looser; then have a number of woollen collars (of different styles if you choose), to button on in the same manner as a linen collar. You can thus keep your neck cool or warm, and can wash the collars, which soil so easily, without washing the whole shirt. The shirt should reach nearly to the knees, to prevent disorders in the stomach and bowels. There are many who will prefer cotton-and-wool goods to all-wool for shirts. The former do not shrink as much, nor are they as expensive, as the latter.
DRAWERS
If you wear drawers, better turn them inside out, so that the seams may not chafe you. They must be loose.
SHOES
You need to exercise more care in the selection of shoes than of any other article of your outfit. Tight boots put an end to all pleasure, if worn on the march; heavy boots or shoes, with enormously thick soles, will weary you; thin boots will not protect the feet sufficiently, and are liable to burst or wear out; Congress boots are apt to bind the cords of the leg, and thus make one lame; short-toed boots or shoes hurt the toes; loose ones do the same by allowing the foot to slide into the toe of the boot or shoe; low-cut shoes continually fill with dust, sand, or mud.
For summer travel, I think you can find nothing better than brogans reaching above the ankles, and fastening by laces or buttons as you prefer, but not so tight as to bind the cords of the foot. See that they bind nowhere except upon the instep. The soles should be wide, and the heels wide and low (about two and three-quarter inches wide by one inch high); have soles and heels well filled with iron nails. Be particular not to have steel nails, which slip so badly on the rocks.
Common brogans, such as are sold in every country-store, are the next best things to walk in; but it is hard to find a pair that will fit a difficult foot, and they readily let in dust and earth.
Whatever you wear, break them in well, and oil the tops thoroughly with neat's-foot oil before you start; and see that there are no nails, either in sight or partly covered, to cut your feet.
False soles are a good thing to have if your shoes will admit them: they help in keeping the feet dry, and in drying the shoes when they are wet.
Woollen or merino stockings are usually preferable to cotton, though for some feet cotton ones are by far the best. Any darning should be done smoothly, since a bunch in the stocking is apt to bruise the skin.
PANTALOONS
Be sure to have the trousers loose, and made of rather heavier cloth than is usually worn at home in summer. They should be cut high in the waist to cover the stomach well, and thus prevent sickness.
The question of wearing "hip-pants," or using suspenders, is worth some attention. The yachting-shirt by custom is worn with hip-pantaloons, and often with a belt around the waist; and this tightening appears to do no mischief to the majority of people. Some, however, find it very uncomfortable, and others are speedily attacked by pains and indigestion in consequence of having a tight waist. If you are in the habit of wearing suspenders, do not change now. If you do not like to wear them over the shirt, you can wear them over a light under-shirt, and have the suspender straps come through small holes in the dress-shirt. In that case cut the holes low enough so that the dress-shirt will fold over the top of the trousers, and give the appearance of hip-pantaloons. If you undertake to wear the suspenders next to the skin, they will gall you. A fortnight's tramping and camping will about ruin a pair of trousers: therefore it is not well to have them made of any thing very expensive.
Camping offers a fine opportunity to wear out old clothes, and to throw them away when you have done with them. You can send home by mail or express your soiled underclothes that are too good to lose or to be washed by your unskilled hands.
CHAPTER V
STOVES AND COOKING-UTENSILS
If you have a permanent camp, or if moving you have wagon-room enough, you will find a stove to be most valuable property. If your party is large it is almost a necessity.
For a permanent camp you can generally get something second-hand at a stove-dealer's or the junk-shop. For the march you will need a stove of sheet iron. About the simplest, smallest, and cheapest thing is a round-cornered box made of sheet iron, eighteen to twenty-four inches long and nine to twelve inches high. It needs no bottom: the ground will answer for that. The top, which is fixed, is a flat piece of sheet iron, with a hole near one end large enough for a pot or pan, and a hole (collar) for the funnel near the other end. It is well also to have a small hole, with a slide to open and close it with, in the end of the box near the bottom, so as to put in wood, and regulate the draught; but you can dispense with the slide by raising the stove from the ground when you want to admit fuel or air.

I have used a more elaborate article than this. It is an old sheet-iron stove that came home from the army, and has since been taken down the coast and around the mountains with parties of ten to twenty. It was almost an indispensable article with such large companies. It is a round-cornered box, twenty-one inches long by twenty wide, and thirteen inches high, with a slide in the front end to admit air and fuel. The bottom is fixed to the body; the top removes, and is fitted loosely to the body after the style of a firkin-cover, i.e., the flange, which is deep and strong, goes outside the stove. There are two holes on the top 5-1/2 inches in diameter, and two 7-1/2 inches, besides the collar for the funnel; and these holes have covers neatly fitted. All of the cooking-utensils and the funnel can be packed inside the stove; and, if you fear it may upset on the march, you can tie the handles of the stove to those of the top piece.
A stove like this will cost about ten dollars; but it is a treasure for a large party or one where there are ladies, or those who object to having their eyes filled with smoke. The coffee-pot and tea-pot for this stove have "sunk bottoms," and hence will boil quicker by presenting more surface to the fire. You should cover the bottom of the stove with four inches or more of earth before making a fire in it.
To prevent the pots and kettles from smutting every thing they touch, each has a separate bag in which it is packed and carried.
The funnel was in five joints, each eighteen inches long, and made upon the "telescope" principle, which is objectionable on account of the smut and the jams the funnel is sure to receive. In practice we have found three lengths sufficient, but have had two elbows made; and with these we can use the stove in an old house, shed, or tent, and secure good draught.
If you have ladies in your party, or those to whom the rough side of camping-out offers few attractions, it is well to consider this stove question. Either of these here described must be handled and transported with care.
A more substantial article is the Dutch oven, now almost unknown in many of the States. It is simply a deep, bailed frying-pan with a heavy cast-iron cover that fits on and overhangs the top. By putting the oven on the coals, and making a fire on the cover, you can bake in it very well. Thousands of these were used by the army during the war, and they are still very extensively used in the South. If their weight is no objection to your plans, I should advise you to have a Dutch oven. They are not expensive if you can find one to buy. If you cannot find one for sale, see if you cannot improvise one in some way by getting a heavy cover for a deep frying-pan. It would be well to try such an improvisation at home before starting, and learn if it will bake or burn, before taking it with you.
Another substitute for a stove is one much used nowadays by camping-parties, and is suited for permanent camps. It is the top of an old cooking-stove, with a length or two of funnel. If you build a good tight fireplace underneath, it answers pretty well. The objection to it is the difficulty of making and keeping the fireplace tight, and it smokes badly when the wind is not favorable for draught. I have seen a great many of these in use, but never knew but one that did well in all weathers, and this had a fireplace nicely built of brick and mortar, and a tight iron door.
Still another article that can be used in permanent camps, or if you have a wagon, is the old-fashioned "Yankee baker," now almost unknown. You can easily find a tinman who has seen and can make one. There is not, however, very often an occasion for baking in camp, or at least most people prefer to fry, boil, or broil.
Camp-stoves are now a regular article of trade; many of them are good, and many are worthless. I cannot undertake to state here the merits or demerits of any particular kind; but before putting money into any I should try to get the advice of some practical man, and not buy any thing with hinged joints or complicated mechanism.


